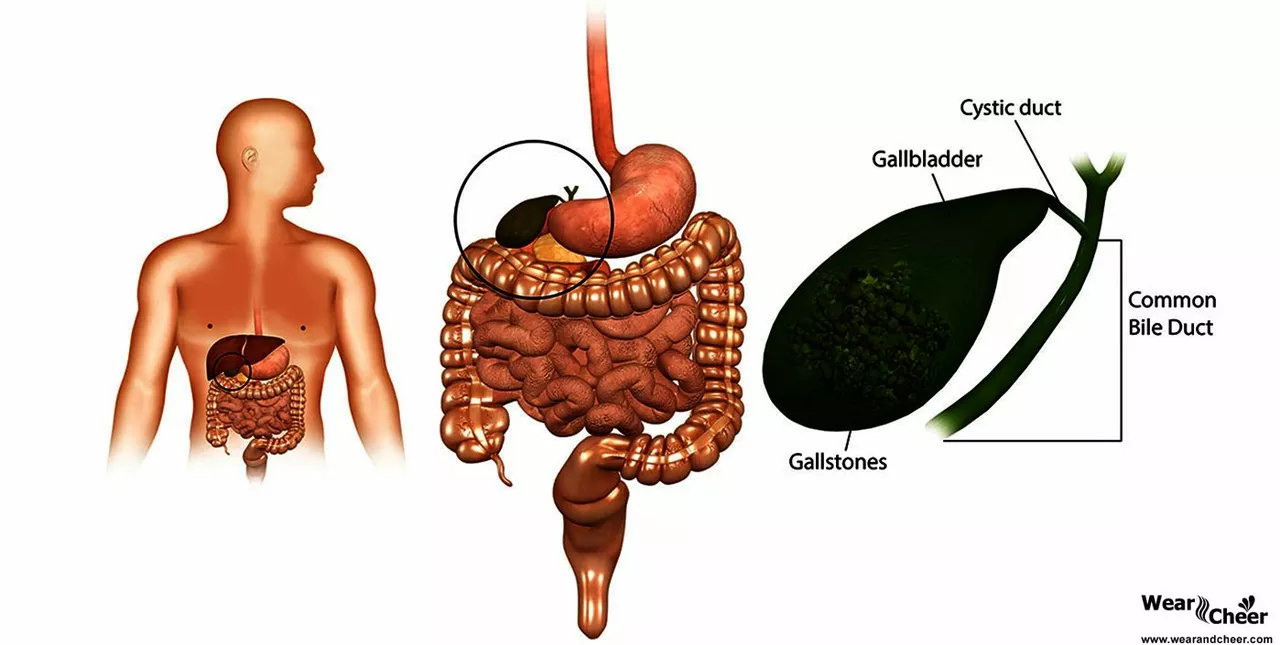
Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms & Simple Ways to Manage Them
If you’ve ever felt a sudden ache in the upper right belly or noticed nausea after a greasy meal, gallstones might be behind it. These tiny crystal clusters form in your gallbladder and can cause anything from mild discomfort to severe pain. Understanding why they appear, how to recognize them early, and what you can actually do about them will save you headaches – and maybe a trip to the ER.
What Triggers Gallstone Formation?
Most gallstones are made of cholesterol, so anything that raises cholesterol in your bile can tip the balance. A diet heavy on saturated fats, rapid weight loss, or prolonged fasting are common culprits. Women, especially those who are pregnant or taking hormone therapy, have a higher risk because estrogen influences cholesterol levels. Genetics play a role too – if close relatives have had gallstones, you’re more likely to develop them.
Besides diet and hormones, certain medical conditions increase the odds. Diabetes, liver disease, and Crohn’s disease can change how your body processes fats, making stone formation easier. Even some medications, like oral contraceptives or cholesterol‑lowering drugs called fibrates, have been linked to higher gallstone rates.
Treatments and Lifestyle Tips
When a stone blocks the bile duct, you’ll feel sharp pain that can last several hours. In those cases, doctors often recommend pain relief and sometimes surgery to remove the gallbladder – a procedure called cholecystectomy. It’s safe, common, and most people recover quickly.
If your stones are small and not causing blockages, you might avoid surgery. Medications containing ursodeoxycholic acid can dissolve cholesterol stones over months, but they’re only effective for certain types. Your doctor will decide based on stone size and composition.
While medical treatment is essential, everyday habits make a big difference. Aim for a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats like olive oil or avocado. Cutting down on fried foods, sugary drinks, and excess cholesterol helps keep bile less saturated.
Staying hydrated is another easy win – drinking enough water keeps bile flowing smoothly. Regular moderate exercise supports weight management without the rapid loss that can trigger stones. If you need to lose weight, aim for a gradual drop of 1–2 pounds per week; crash diets are counterproductive.
Finally, watch for warning signs: sudden, intense abdominal pain; fever with chills; jaundice (yellow skin); or dark urine. Those symptoms suggest a possible blockage or infection and require prompt medical attention.
By knowing what fuels gallstone growth and taking practical steps – smarter eating, steady activity, and regular check‑ups – you can keep your gallbladder running smoothly and avoid painful surprises down the road.
Gallstones and IBS: Understanding the Connection and Managing Symptoms
In my recent research on gallstones and IBS, I discovered that there is a significant connection between the two conditions. Both are digestive disorders and share several common symptoms, such as abdominal pain and bloating. It's essential to understand this link to effectively manage the symptoms and avoid complications. A combination of dietary changes, stress management, and medical treatment can help alleviate the discomfort. Stay tuned for more in-depth information about managing gallstones and IBS in upcoming blog posts.